- HOME >> SOLUTIONS >> By Standard >> ISO Test Standards
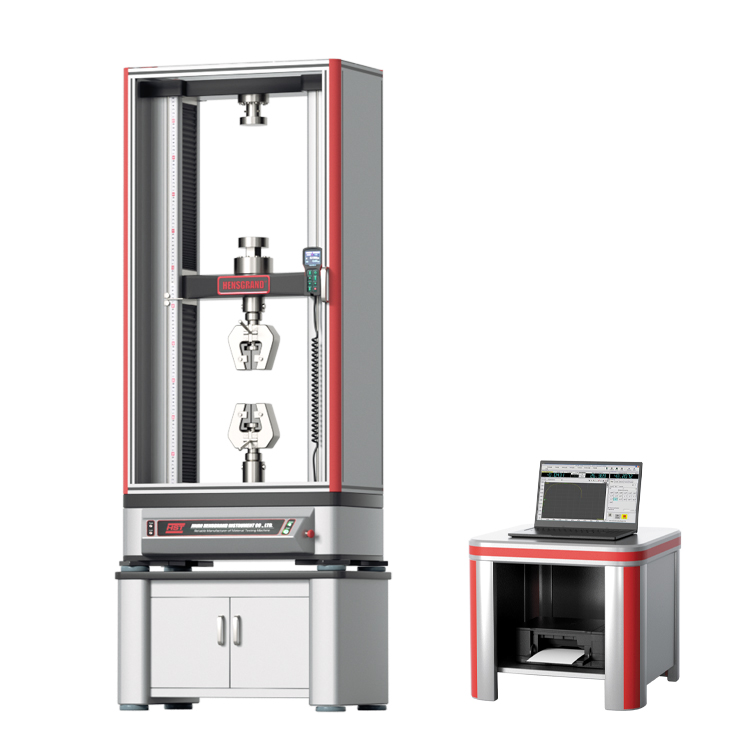
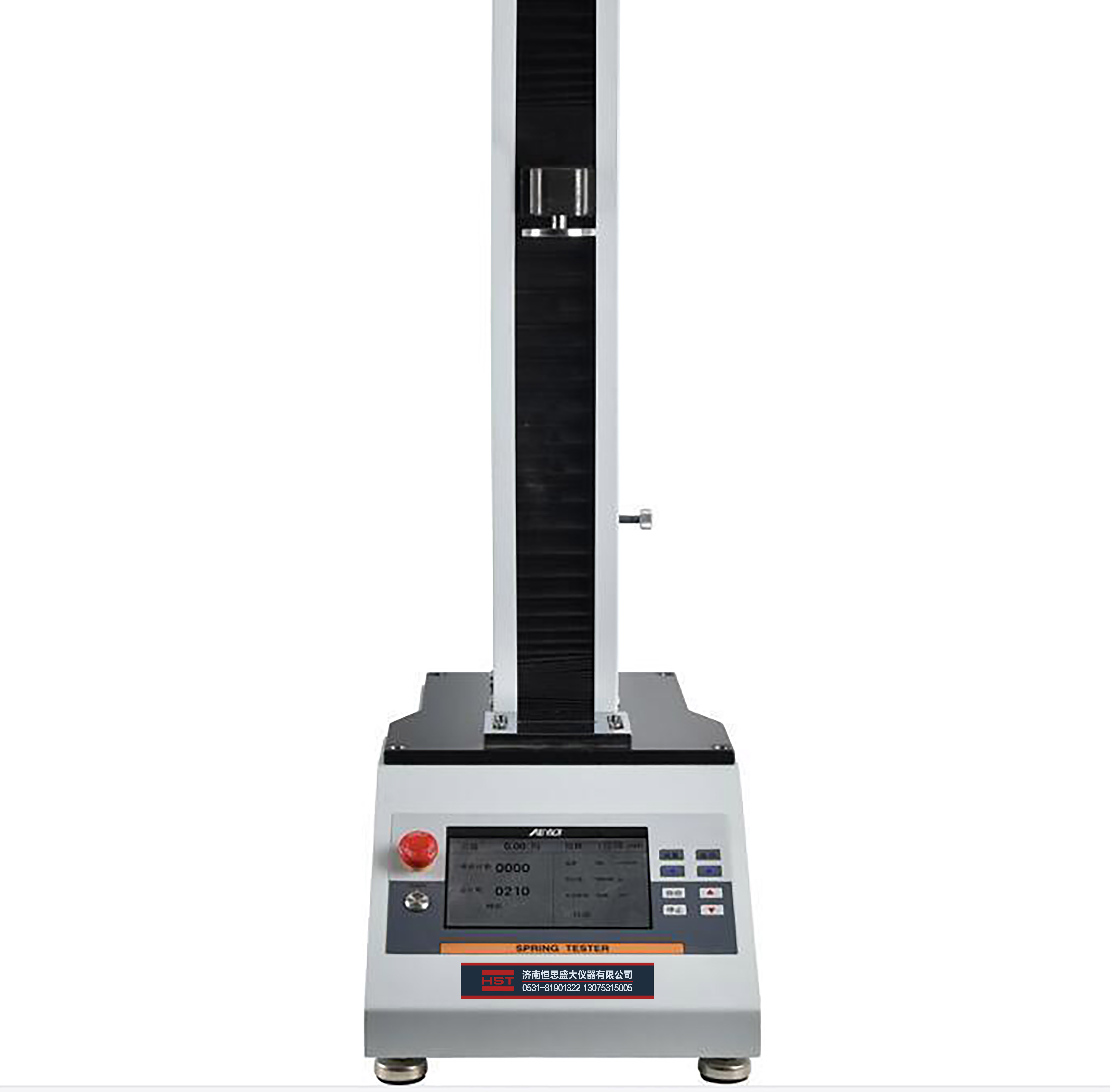
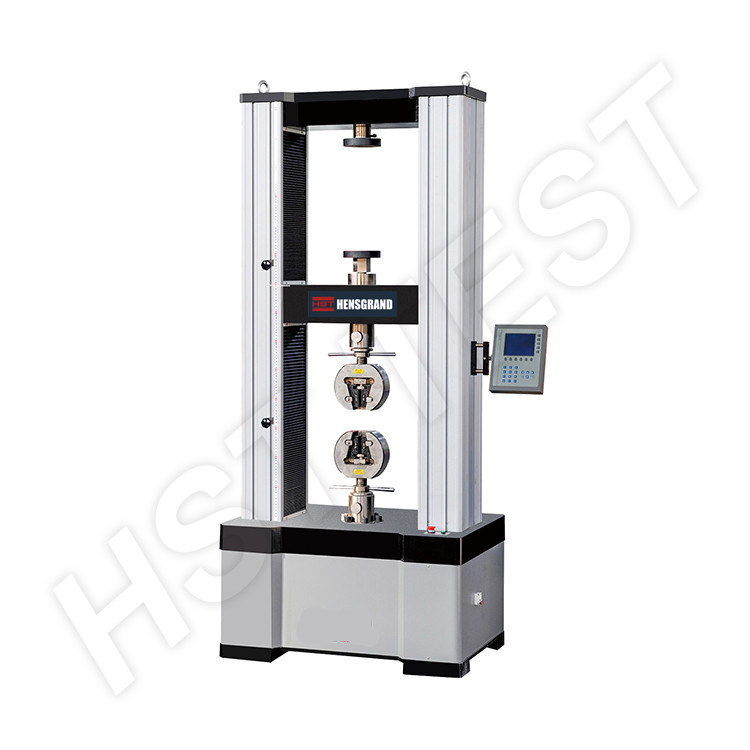
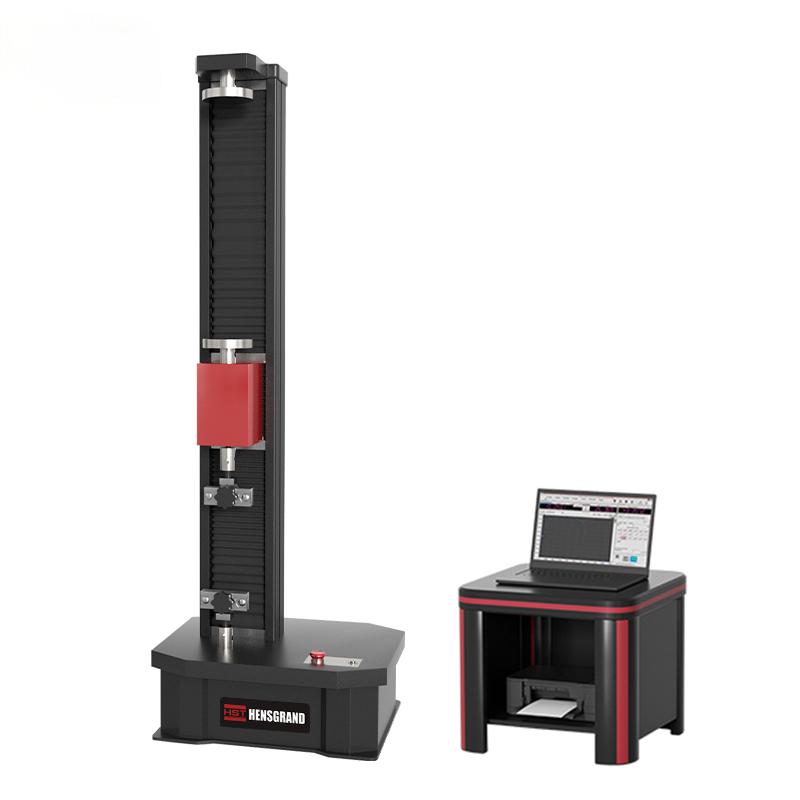
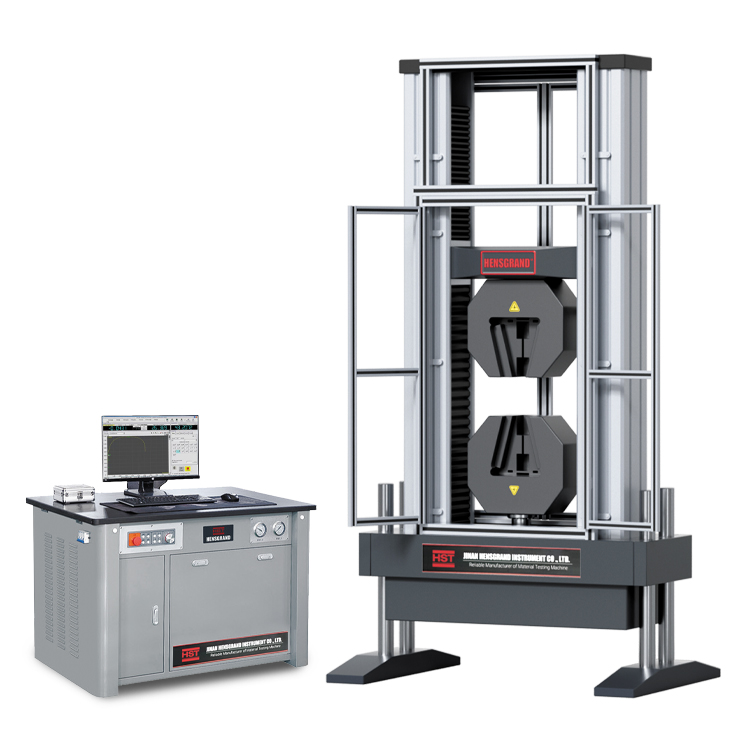
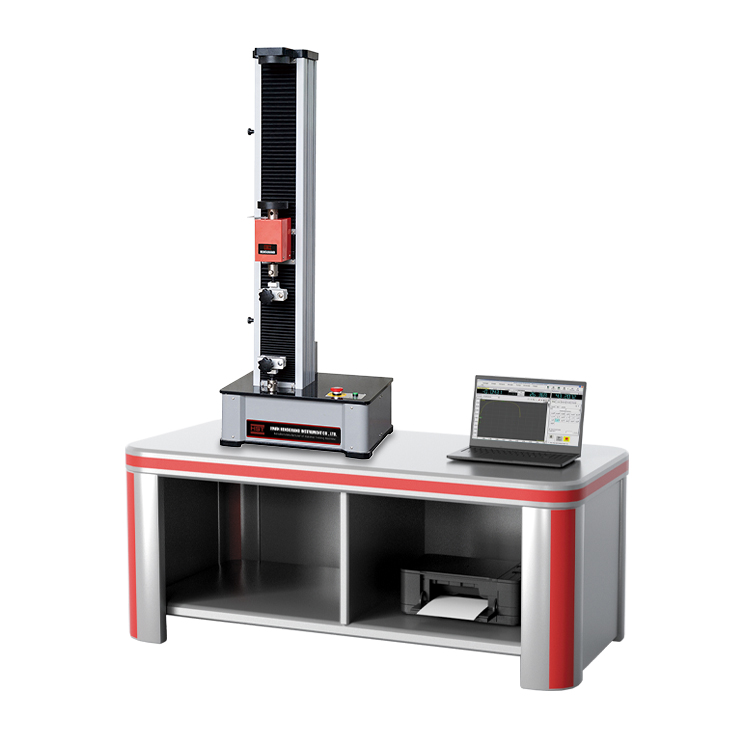
ISO 6892 Tensile Testing of Metallic Materials
ISO 6892-1 is one of the most commonly adopted testing standards for the tensile testing of metallic materials at ambient temperature. ISO 6892-1:2016 is the current version of a metals testing standard that has undergone several iterations. Instron actively participates on the committee, which allows us to ensure that our products are compliant with the standard and that our team is educated about upcoming changes.
The third edition, released in 2019, is the most recent version of this standard and cancels and replaces the second edition (ISO 6892-1:2016). Only minor changes and corrections have been introduced into the latest version. These updates are enumerated in the forward of the latest standard. The second edition introduced a much more significant revision in the description of three different test methods: Method A1, Method A2, and Method B.
ISO 6892-1 is similar but not equivalent to ASTM E8/E8M. This guide is designed to introduce you to the basic elements of an ISO 6892-1 tensile test and will provide an overview of the materials testing equipment, software, and tensile specimens needed. However, anyone planning to conduct testing should not consider this guide an adequate substitute for reading the full standard.
What Does it Measure?
ISO 6892-1 measures the tensile properties of metallic materials in any form at an ambient temperature. Tests carried out under controlled conditions must be made at a temperature of 23 degrees Celsius plus or minus 5 degrees. For testing at elevated temperatures, please refer to ISO 6892-2. ISO 6892-1 measures many different tensile properties, with the following being the most common:
Yield Strength - The stress at which a material becomes permanently deformed. ISO 6892-1 determines both upper and lower yield strength: depending on the yielding phenomena, ISO 6892-1 specifies both upper and lower yield strength requirements for discontinuously yielding material and the offset yield method for continuously-yielding material.
Yield Point Elongation - Only suitable for discontinuously yielding material, the Yield Point Elongation is the difference between the elongation of the specimen at the start and at the finish of discontinuous yielding (the area in which an increase in strain occurs without an increase in stress).
Tensile Strength - The maximum force or stress that a material is capable of sustaining during a tensile test.
Reduction of Area - A measurement of the ductility of a material. This is the difference between the original cross sectional area of a specimen and the area of its smallest cross section after testing, usually expressed as a percentage decrease in original cross section. The smallest cross section can be measured at or after fracture.
The third edition, released in 2019, is the most recent version of this standard and cancels and replaces the second edition (ISO 6892-1:2016). Only minor changes and corrections have been introduced into the latest version. These updates are enumerated in the forward of the latest standard. The second edition introduced a much more significant revision in the description of three different test methods: Method A1, Method A2, and Method B.
ISO 6892-1 is similar but not equivalent to ASTM E8/E8M. This guide is designed to introduce you to the basic elements of an ISO 6892-1 tensile test and will provide an overview of the materials testing equipment, software, and tensile specimens needed. However, anyone planning to conduct testing should not consider this guide an adequate substitute for reading the full standard.
What Does it Measure?
ISO 6892-1 measures the tensile properties of metallic materials in any form at an ambient temperature. Tests carried out under controlled conditions must be made at a temperature of 23 degrees Celsius plus or minus 5 degrees. For testing at elevated temperatures, please refer to ISO 6892-2. ISO 6892-1 measures many different tensile properties, with the following being the most common:
Yield Strength - The stress at which a material becomes permanently deformed. ISO 6892-1 determines both upper and lower yield strength: depending on the yielding phenomena, ISO 6892-1 specifies both upper and lower yield strength requirements for discontinuously yielding material and the offset yield method for continuously-yielding material.
Yield Point Elongation - Only suitable for discontinuously yielding material, the Yield Point Elongation is the difference between the elongation of the specimen at the start and at the finish of discontinuous yielding (the area in which an increase in strain occurs without an increase in stress).
Tensile Strength - The maximum force or stress that a material is capable of sustaining during a tensile test.
Reduction of Area - A measurement of the ductility of a material. This is the difference between the original cross sectional area of a specimen and the area of its smallest cross section after testing, usually expressed as a percentage decrease in original cross section. The smallest cross section can be measured at or after fracture.