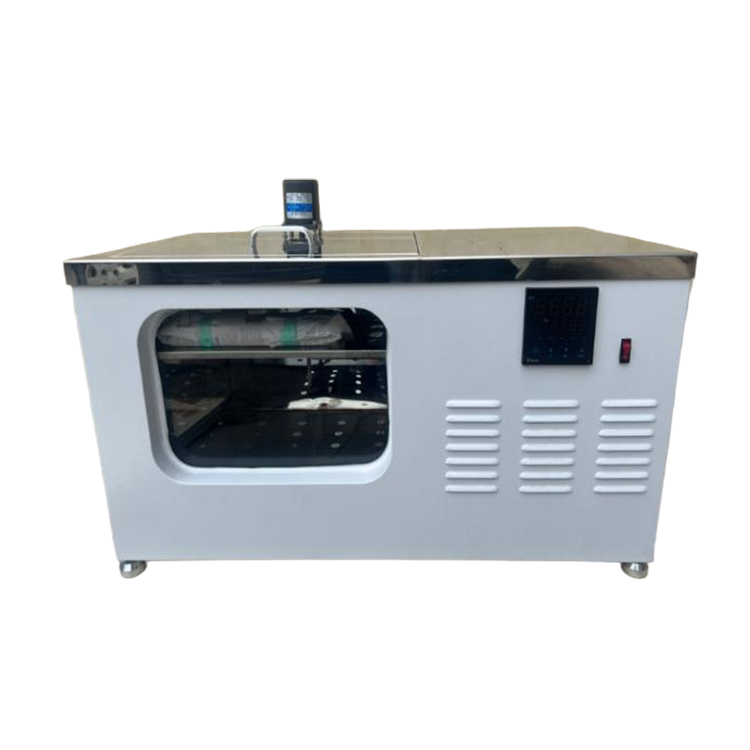
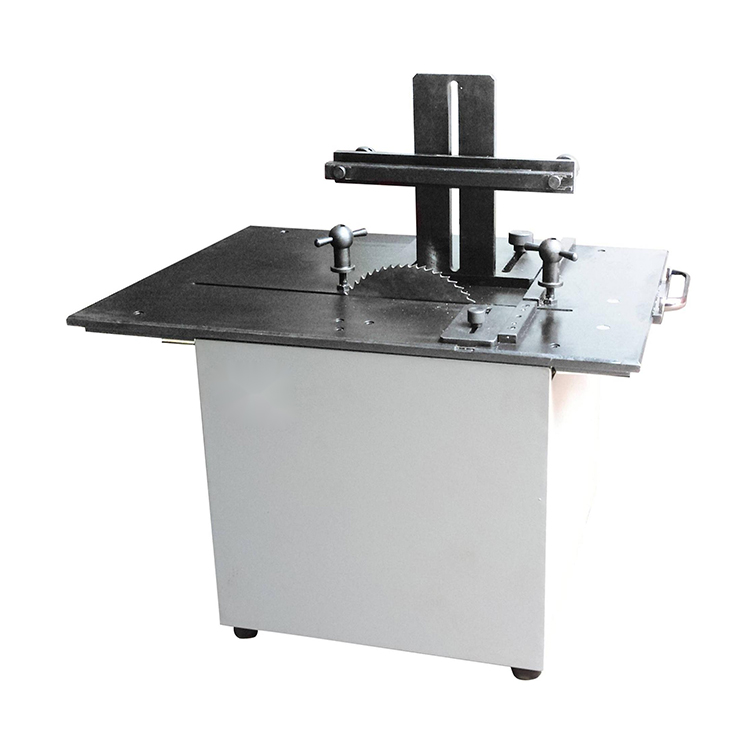
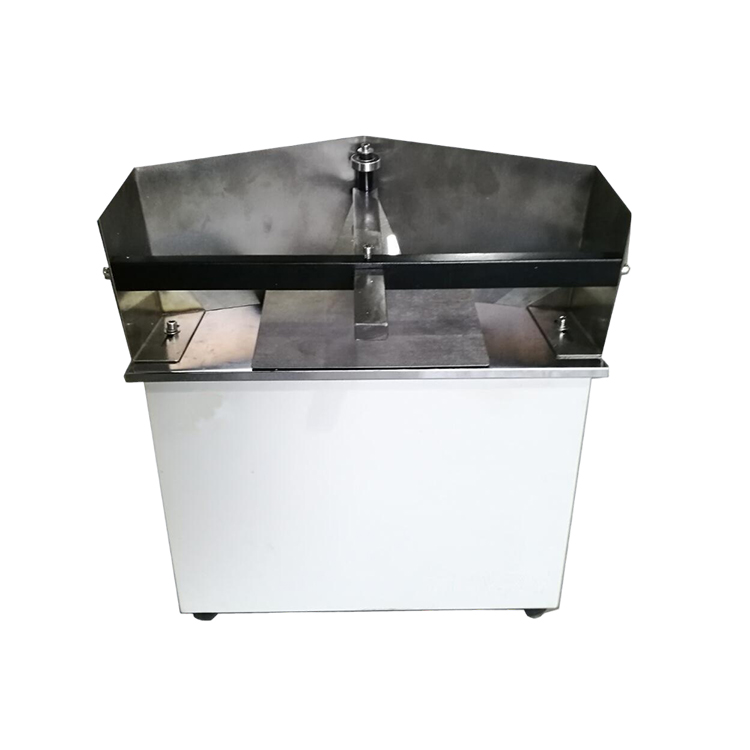
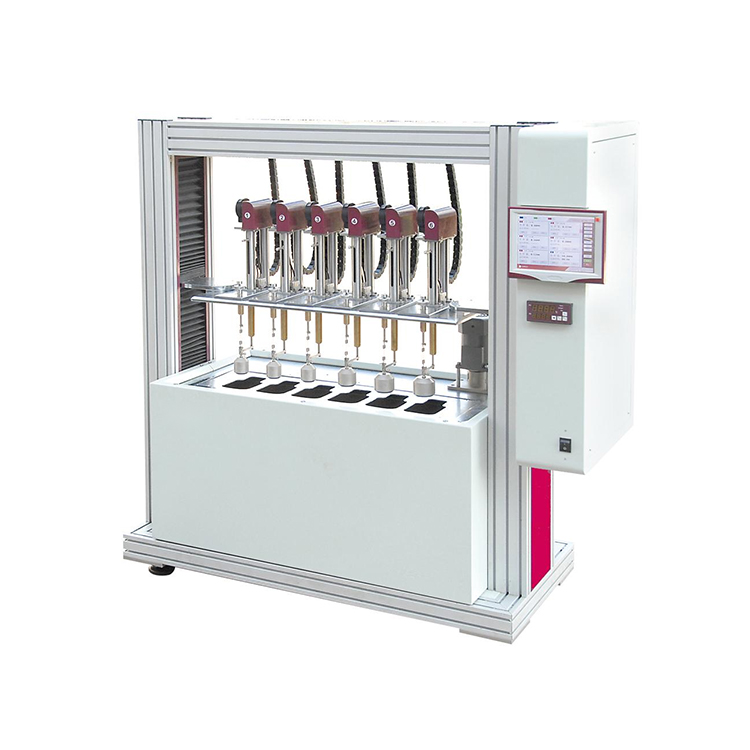
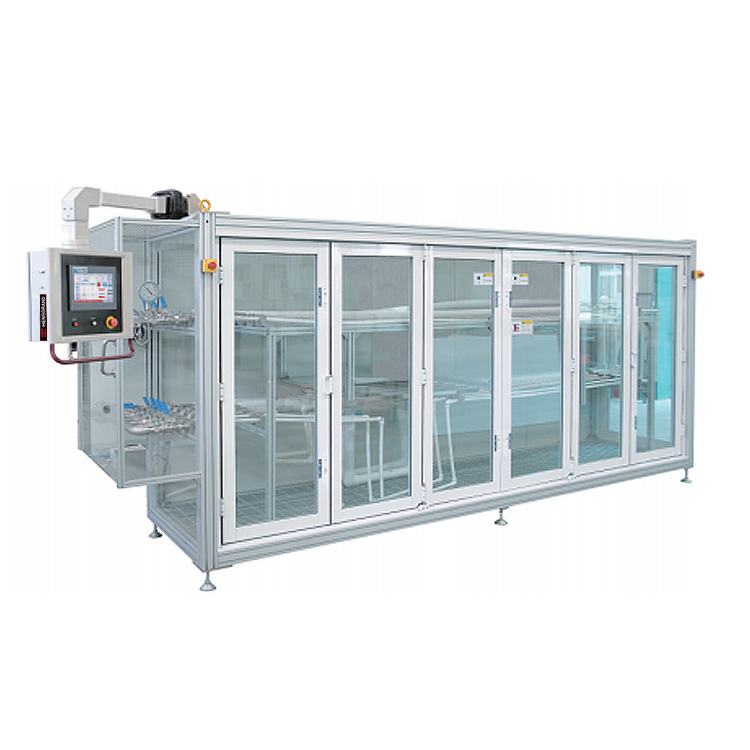
HST-SCR35 Environmental Stress Cracking Resistance Testing Machine

The environmental stress cracking (ESC) apparatus is suitable for determining the ESCC resistance of polyethylene homopolymers and other copolymers containing less than 50% (m/m) of 1-olefin monomers
Standards:
GB/T1842, GB/T2951.41, ASTM D1693
Request A Quote Files DownloadIntroduction
The environmental stress cracking (ESC) apparatus is suitable for determining the ESCC resistance of polyethylene homopolymers and other copolymers containing less than 50% (m/m) of 1-olefin monomers and no more than 3% (m/m) of functional non-olefin monomers under specified conditions. This apparatus, designed by our company based on the recommendations of GB/T1842-2008, "Polyethylene Plastics Test Method for Environmental Stress Cracking," and ASTM D1693:2008, "Standard Test Method for Environmental Stress Cracking of Ethylene Plastics," is used to determine how the stress acting on the specimen and the thermal history of the specimen affect the ESCC resistance of the material.
Rated Specifications
Ambient Operating Temperature: 10°C to 35°C
Specimen Dimensions (Length* Width* Thickness): (38* 13* Thickness) mm (See attached table for thickness)
Score Length: 19±0.1 mm
Specimen Holder: Inner Groove Width 12 mm, Outer Groove Width 16 mm, Height 10 mm
Constant Temperature Range: 50°C±0.5°C and 100°C±0.5°C
Glass Tube Specifications:φ30-32 mm×200 mm
Water Temperature Control Accuracy:±0.5°C
Score Blade Height: 3 mm
Number of Glass Tubes: 5
Window Dimensions: 360 mm* 240 mm